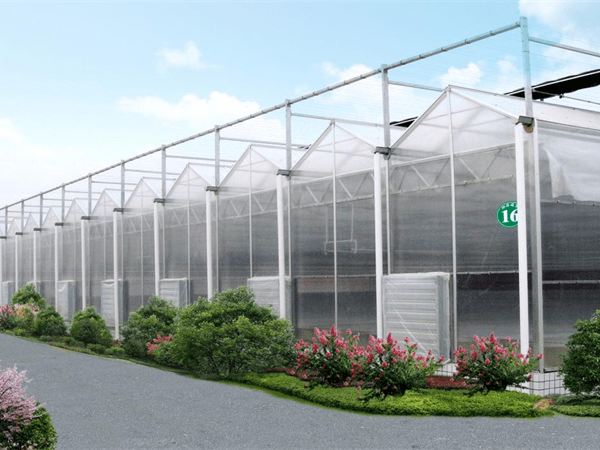
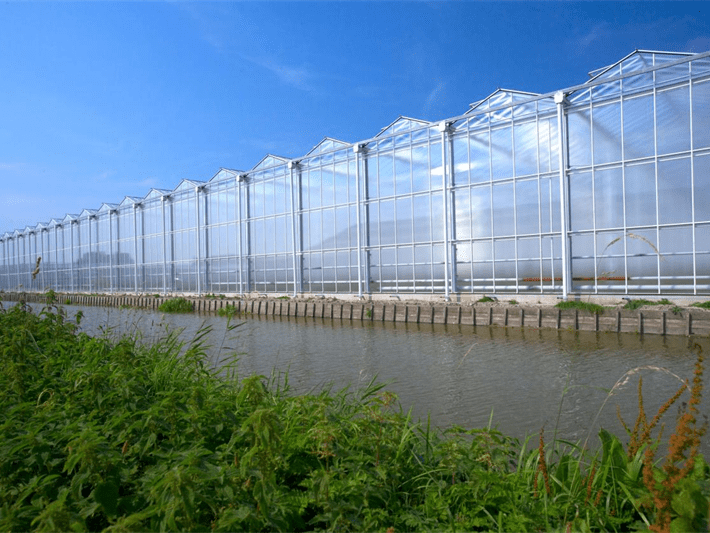
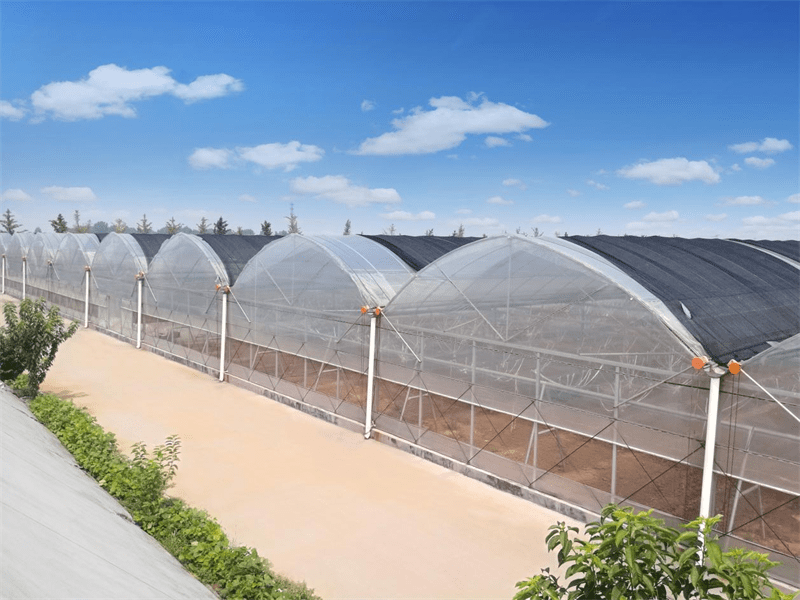
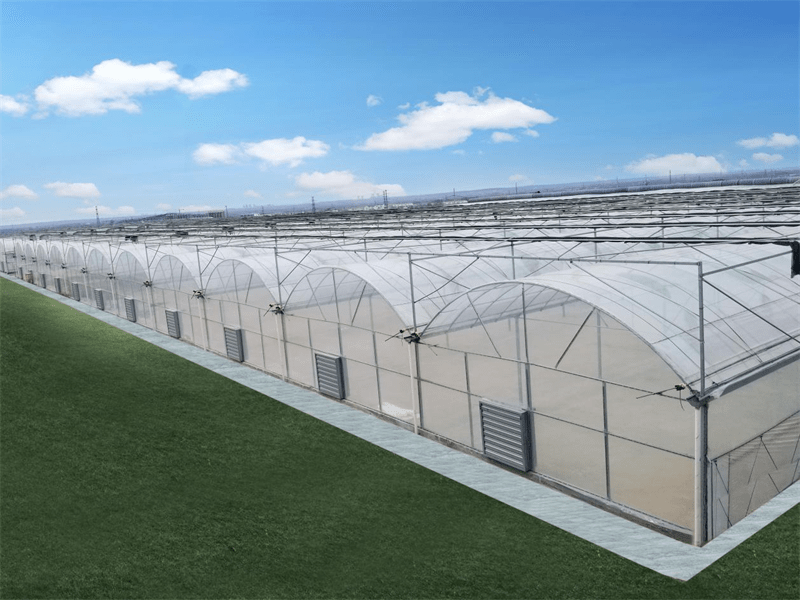
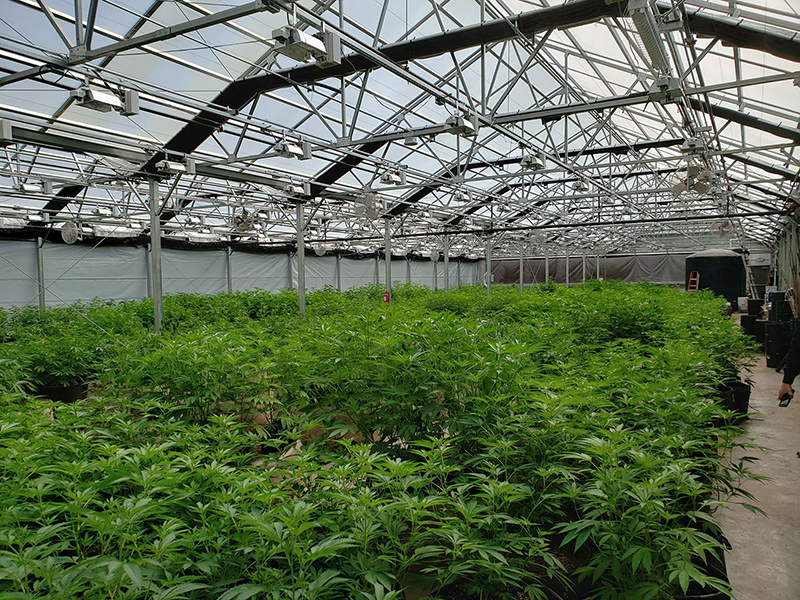
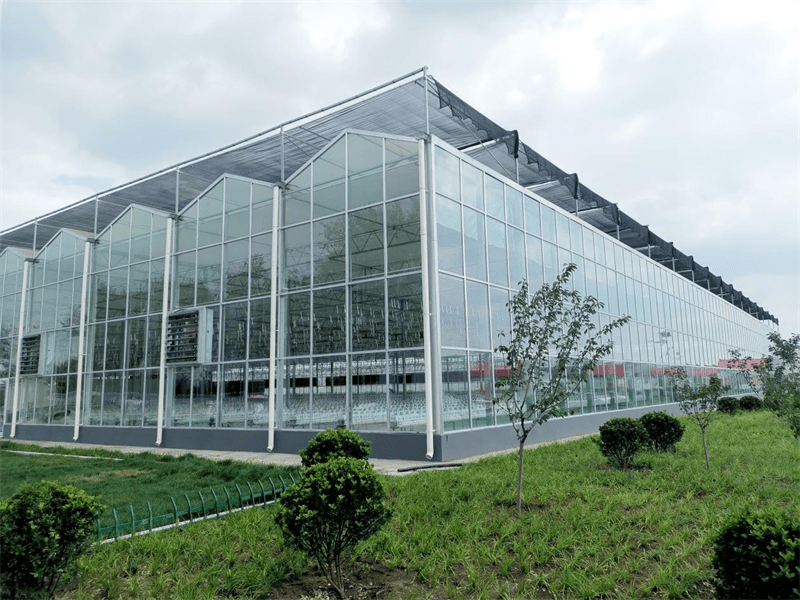
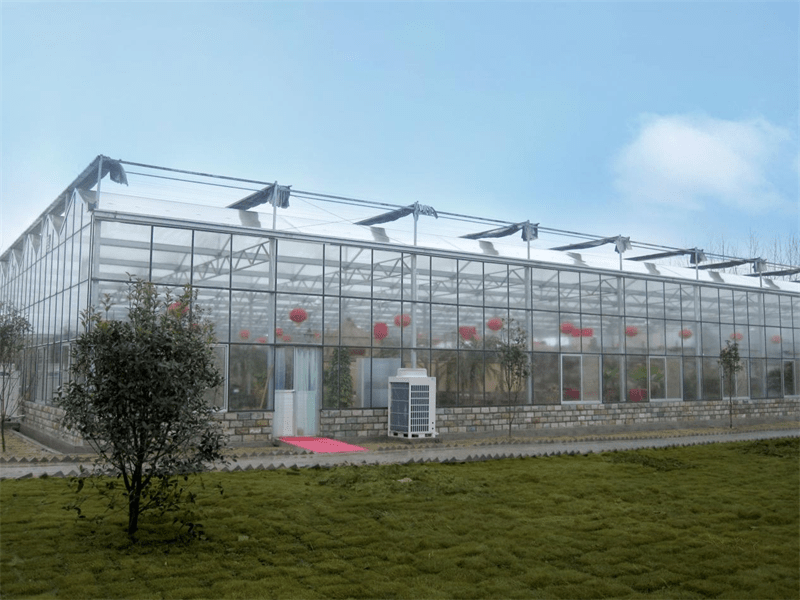
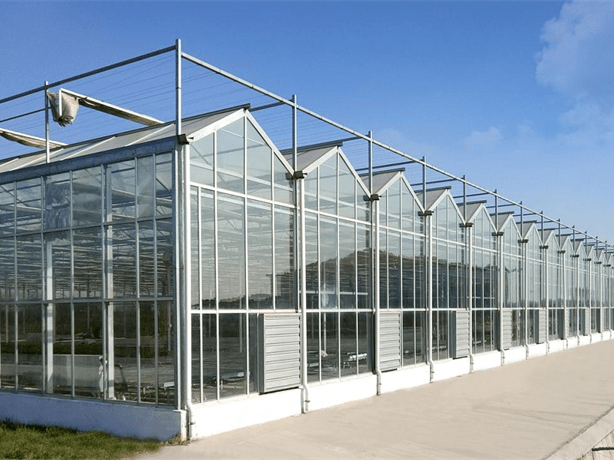
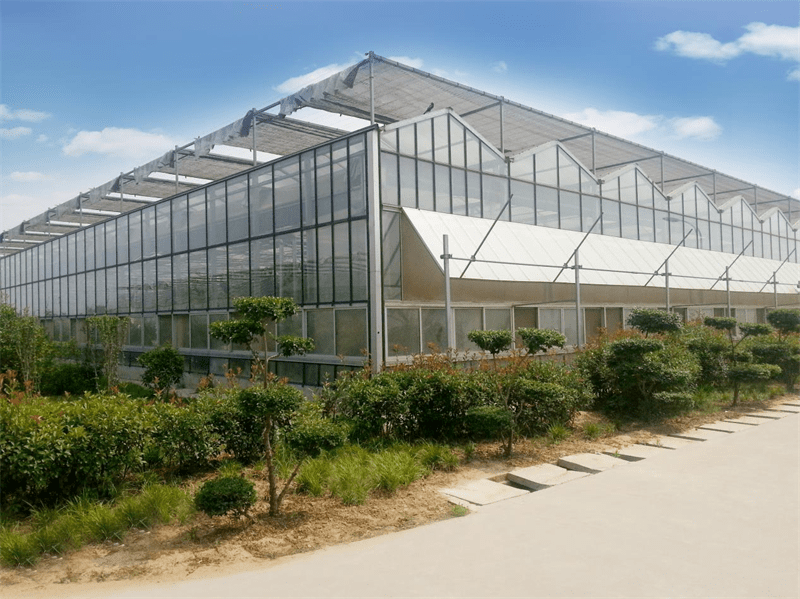
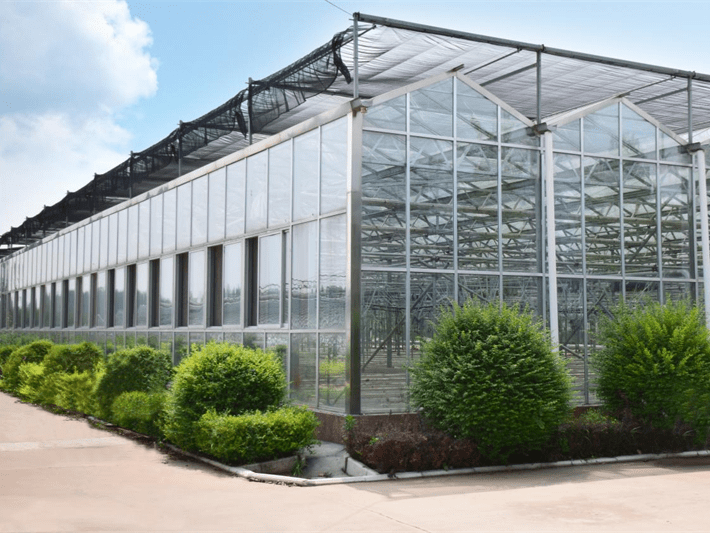
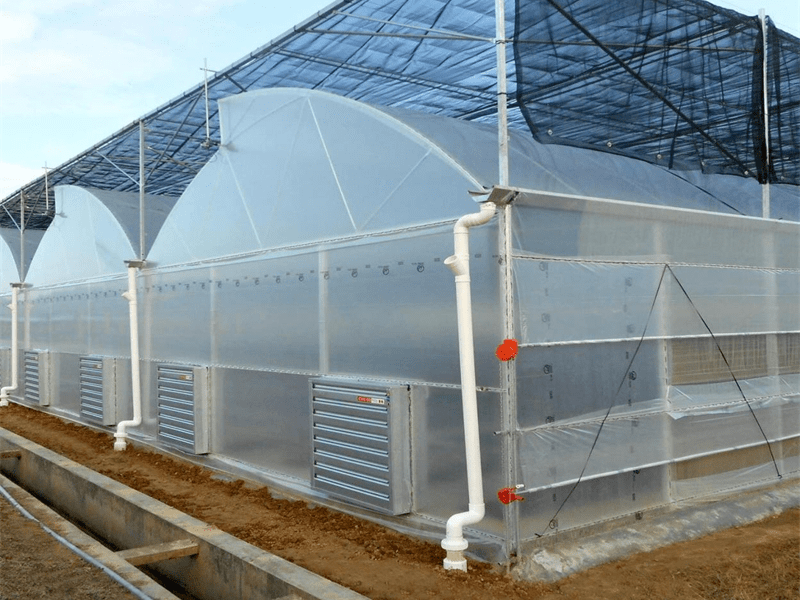
Glass Greenhouse With Outer Sunshade System And Hydroponic System
description2
Characteristics of Glass Greenhouse
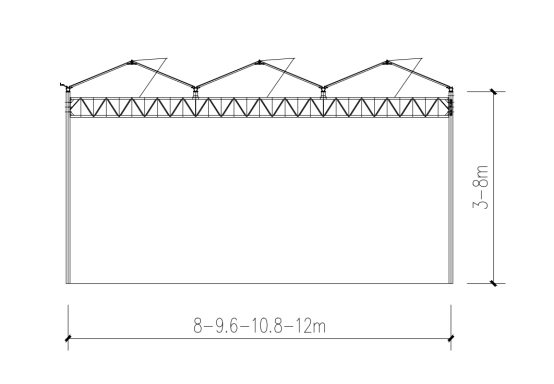
Parameters
| Type | Multi-Span Glass Greenhouse |
| Span Width | 8m/9.6m/10.8m/12m |
| Bay width | 4m / 8m |
| Gutter hight | 3-8m |
| Snow load | 0.5KN/M2 |
| Wind load | 0.6KN/M2 |
| Hanging load | 15KG/M2 |
| Max rainfall discharge | 140 mm/h |
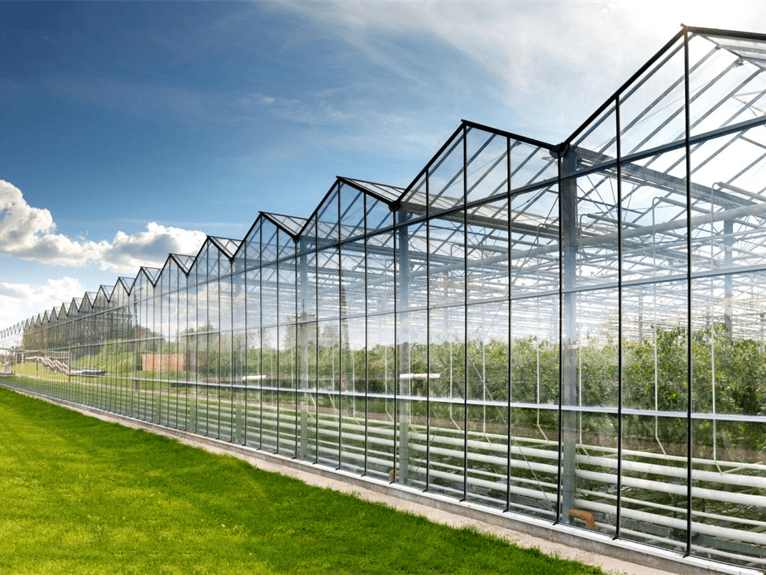
Greenhouse Cover&Structure
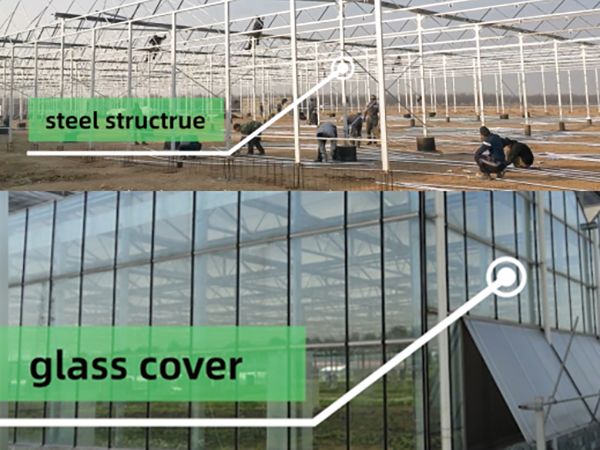

- 1. Steel Structure
- The steel structure is made of high-quality carbon steel that meets national standards, and the parts and fasteners are processed according to specific technical requirements for hot-galvanized steel production. The hot galvanized steel should meet national standards for quality products, with the galvanized layer having uniform thickness, no burrs, and a minimum thickness of 60um.
- 2. Cover material
- The glass covering typically consists of tempered glass panels with thickness options of 4mm, 5mm, or 6mm for the roof, and hollow glass panels with float glass or tempered glass and thicknesses of 4+6+4mm or 5+6+5mm for the sides. Specialized aluminum profiles are used to securely fasten the glass components in place.
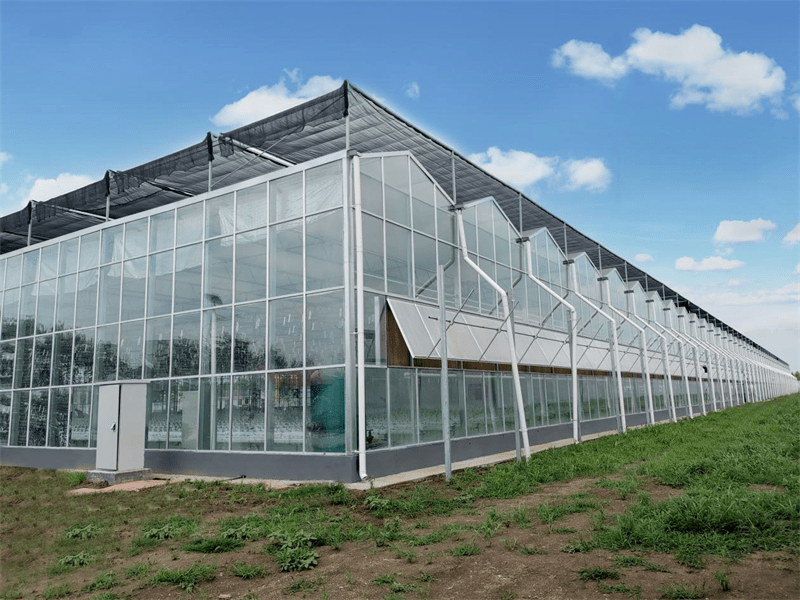
Outer Sunshade System
In the summer when indoor temperature rise to a certain value, it can reflect a part of the sun and diffuse sunshine into the greenhouse according to the different shading rate, achieving the purpose of cooling temperature. Close sunshade screen, at the same time the greenhouse temperature drop 4 ~ 6℃, reduce temperature in the greenhouse. By choosing different shading rate curtain, it can meet the sunshine demand of different crops.
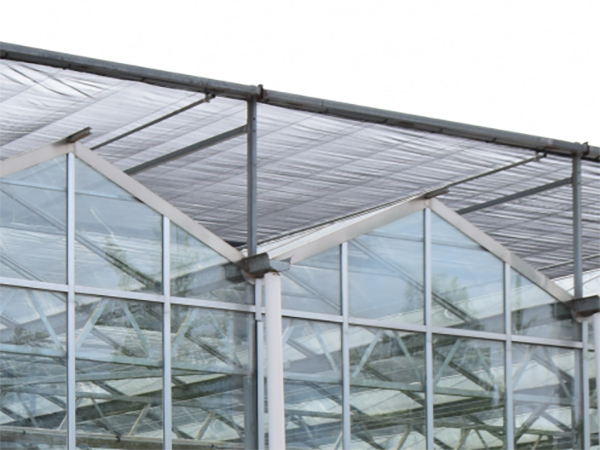

Inner Sunshade&Warming System
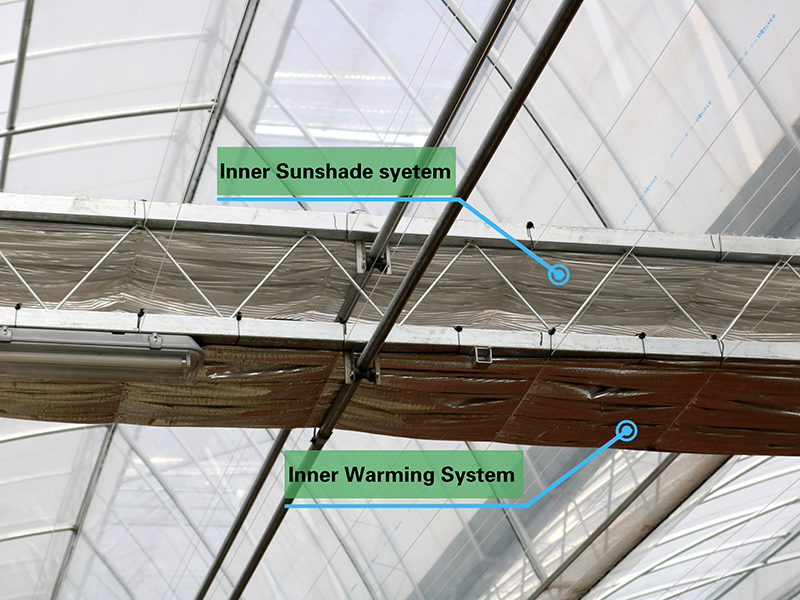
The system involves the installation of an inner sunshade net in the greenhouse to provide temperature control. During the summer, it has the ability to lower the internal temperature, while in winter and at night, it functions to retain heat. Additionally, the system offers two variations: ventilation-type and thermal insulation-type, allowing for flexibility in managing the greenhouse environment.
An internal thermal insulation curtain system is mainly used in cold regions with temperatures below 5°C. It helps to reduce heat loss through infrared radiation during cold nights, which in turn lowers surface heat loss and decreases energy consumption for heating. This can result in reduced operating costs for greenhouses.
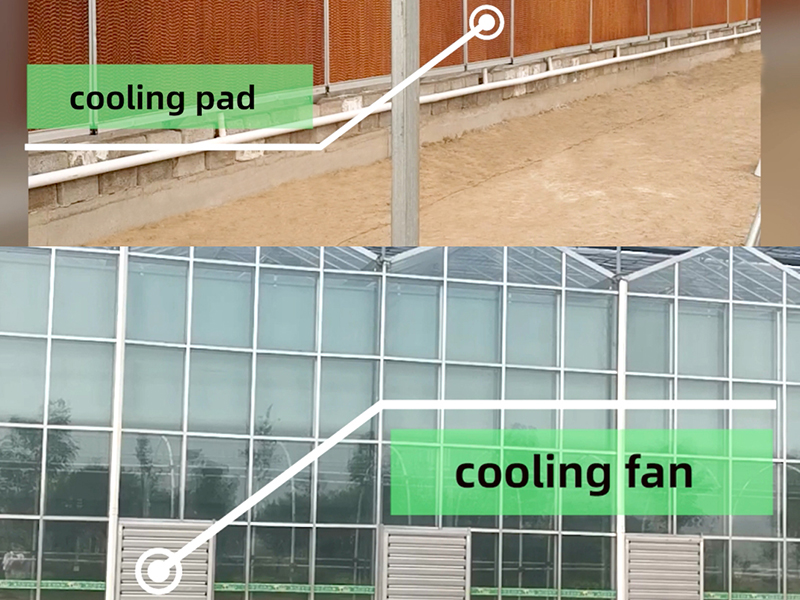
Cooling System
The cooling system utilizes water evaporation to reduce temperature. It includes high-quality cooling pads and powerful fans. The central component of the cooling system is the evaporative cooling pads, made of corrugated fiber paper that is corrosion-resistant and long-lasting due to a special chemical composition in the raw material. These pads ensure thorough saturation with water. As air passes through the pads, the exchange of water and air transforms hot air into cool air while also humidifying and cooling the air.
Ventilation System
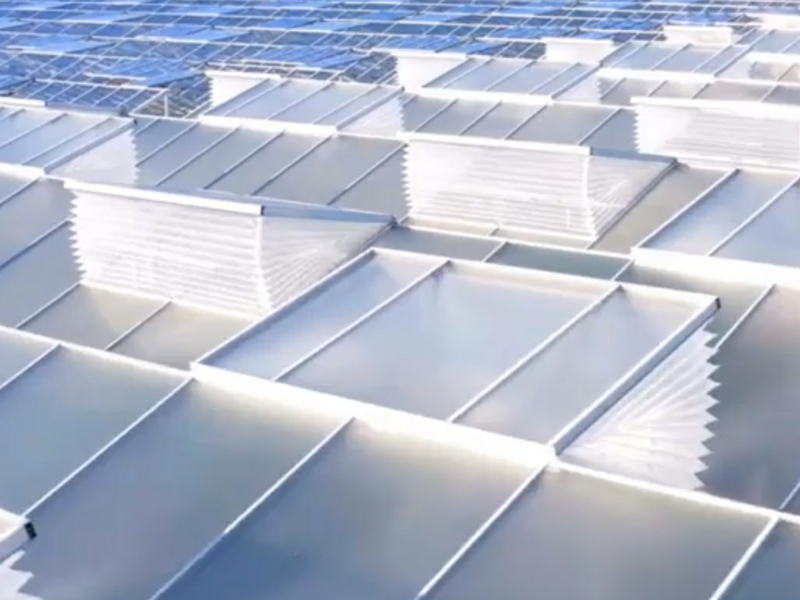

There are two main types of greenhouse ventilation systems: natural ventilation and forced ventilation. For natural ventilation in film greenhouses, roll membrane ventilation is used on the roof and sides, while for sawtooth greenhouses, the primary form of roof ventilation is roll film ventilation. Insect-proof nets with a mesh size of 60 are placed at the ventilation openings to prevent insects from entering. The ventilation systems can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of customers and the conditions for growing plants.
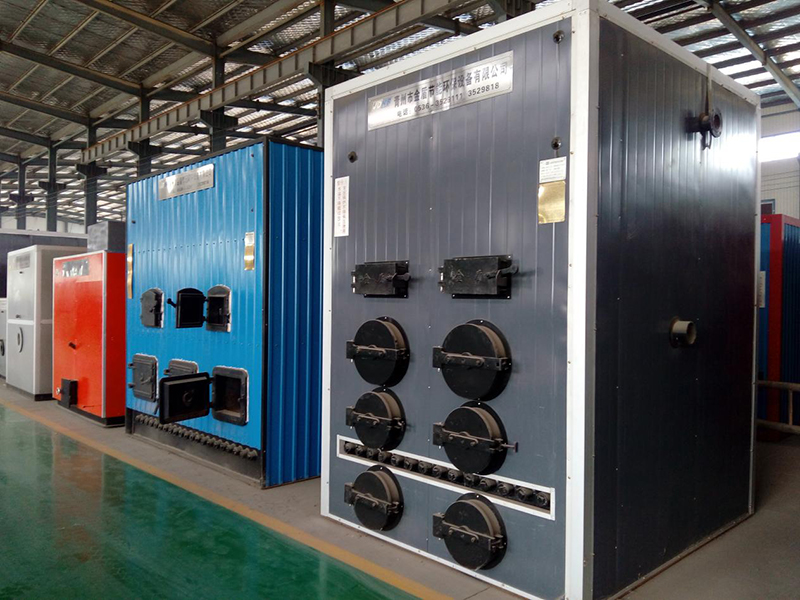
Heating System
The heating system can be categorized into two types: one utilizes a boiler for heat production, while the other relies on electricity. Boilers can be fueled by coal, oil, gas, or biofuels. To operate boilers, pipelines need to be laid and a water warming blower is required for heating. Alternatively, if electricity is used as the heat source, an electric warm air blower is necessary.

Light Compensating System
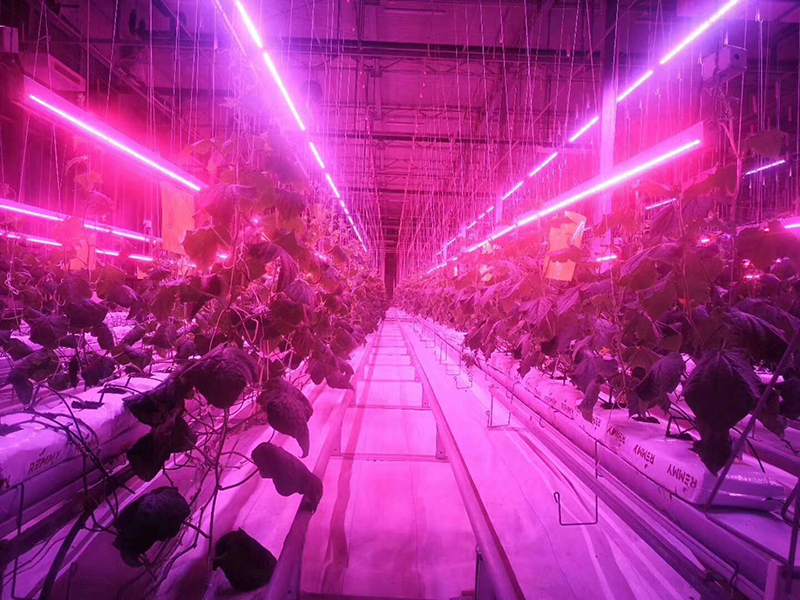

Greenhouse compensating light, also known as plant light, is a necessary artificial light source used to provide plants with the light they need for growth and development when natural sunlight is not available. This concept is based on the natural laws of plant growth and the principle of plants using sunlight for photosynthesis. Currently, the majority of farmers rely on high pressure sodium lamps and LED lamps to provide this crucial light to their plants.
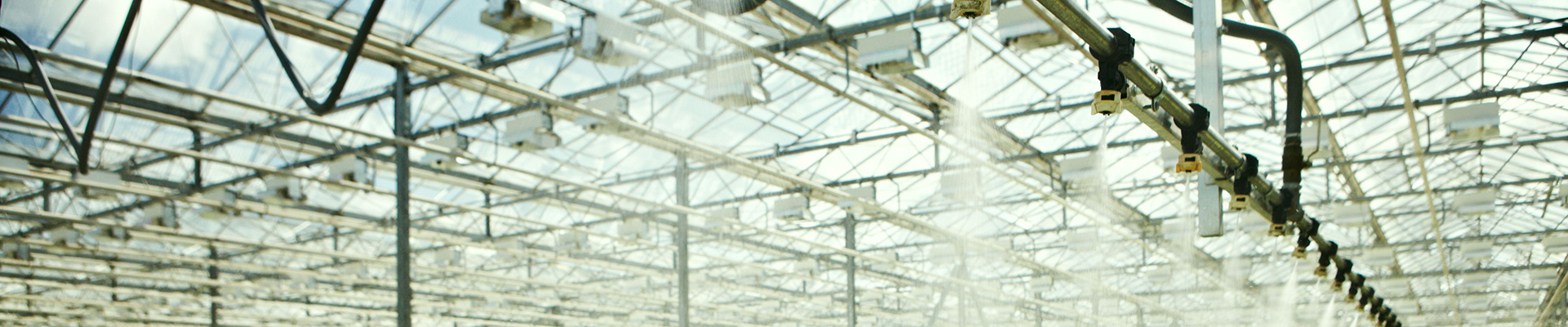
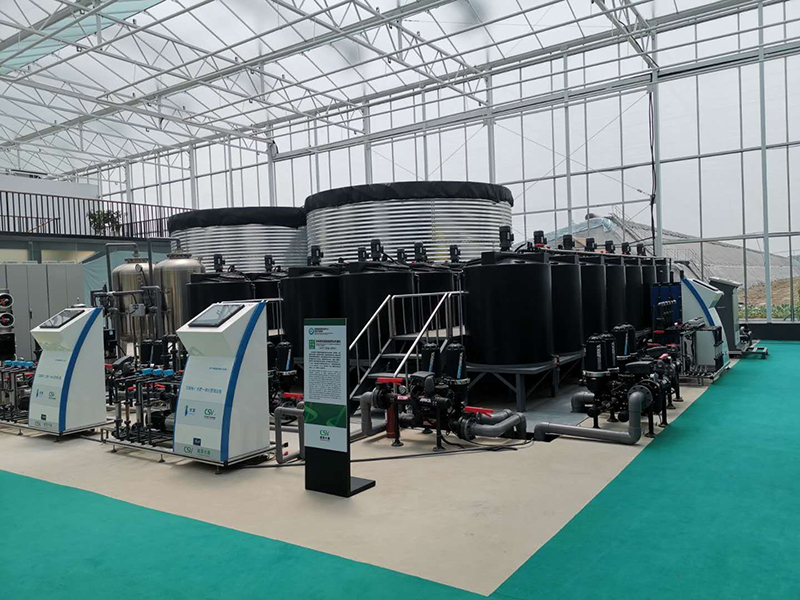
Irrigation System
The greenhouse irrigation system consists of a water purification system, water storage tank, irrigation system, and water and fertilizer integrated machine. We offer two types of irrigation systems: drip irrigation and spray irrigation, allowing you to select the most suitable option for your greenhouse.

Nursery Bed System
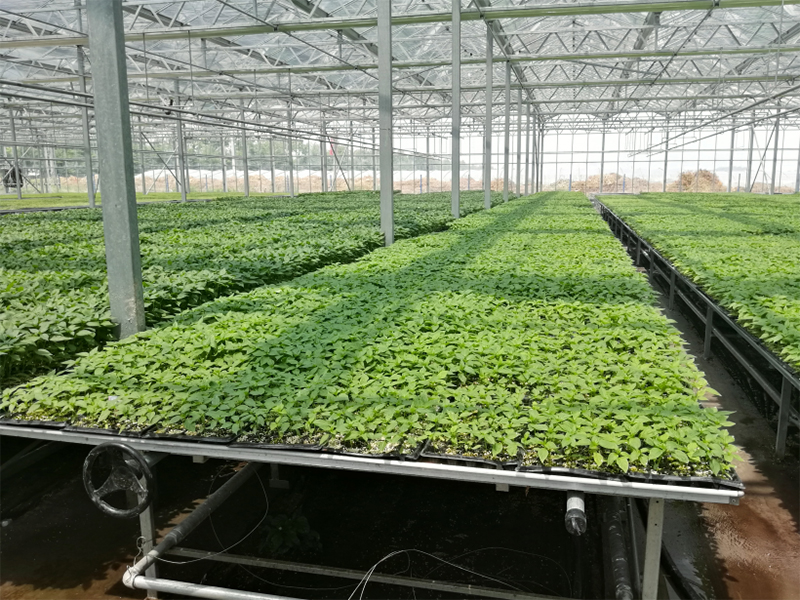

The nursery bed comprises both a fixed bed and a movable bed. The specifications for the movable nursery bed include a seedbed standard height of 0.75m, with adjustable options. It has a standard width of 1.65m, which can be modified to suit the greenhouse's width, and its length can be tailored to meet user requirements. The movable bed grid measures 130mm x 30mm (length x width) and is constructed from hot-dip galvanized material, offering high corrosion resistance, excellent load-bearing capacity, and a long service life. Additionally, the specifications for the fixed bed are as follows: length of 16m, width of 1.4m, and a height of 0.75m.
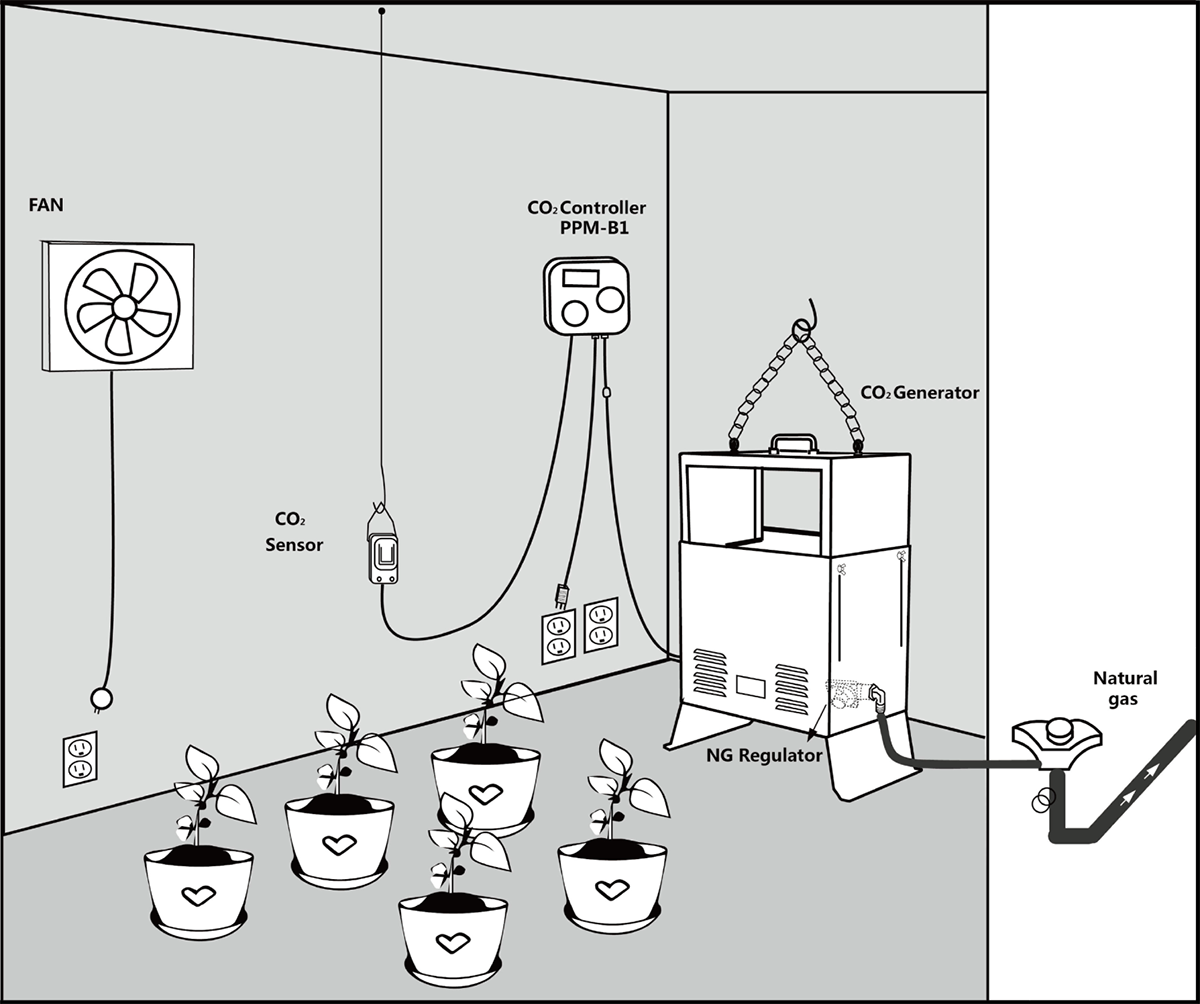
CO2 Control System
The primary goal is to monitor the CO2 concentration in the greenhouse in real-time to maintain levels suitable for crop growth. This is primarily achieved through the use of a CO2 detector and a CO2 generator. The CO2 sensor is a device designed to detect CO2 concentration, allowing for continuous monitoring of environmental parameters within the greenhouse and enabling adjustments to be made based on the monitoring results to create an optimal environment for plant growth.
Control System

The greenhouse control system typically consists of a control cabinet, sensors, and circuits. These components work together to facilitate semi-automatic control of the system, making it easier to manage. Additionally, it's possible to employ computer networking to enable intelligent control of the greenhouse systems, enhancing their functionality and efficiency.