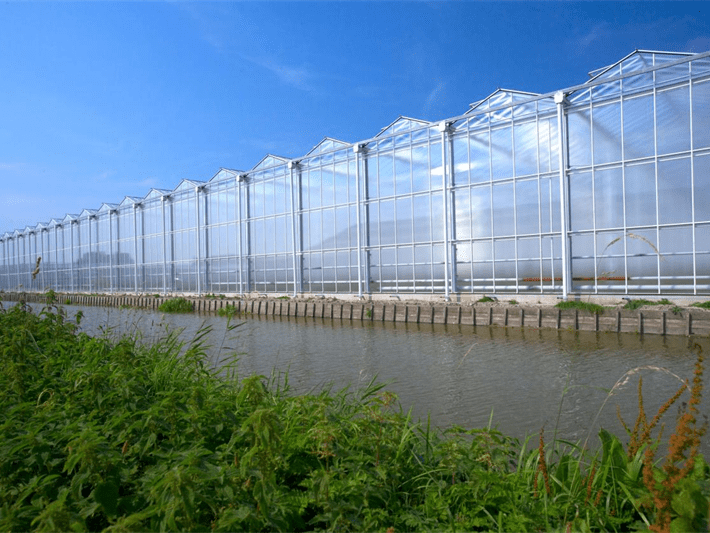
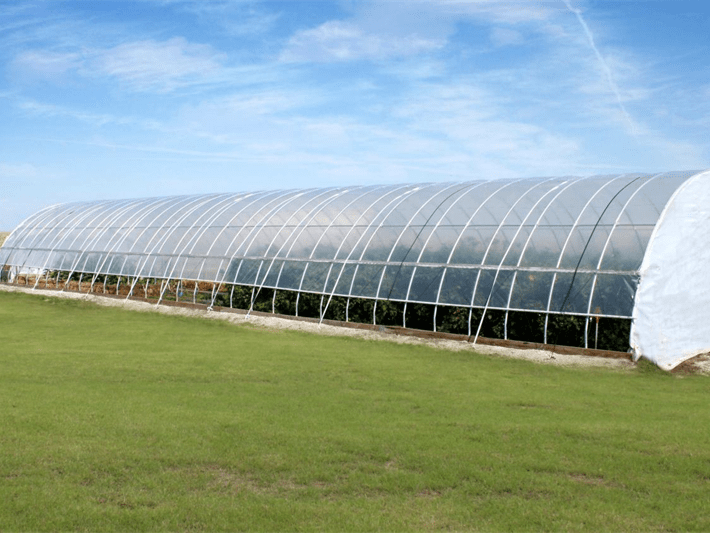
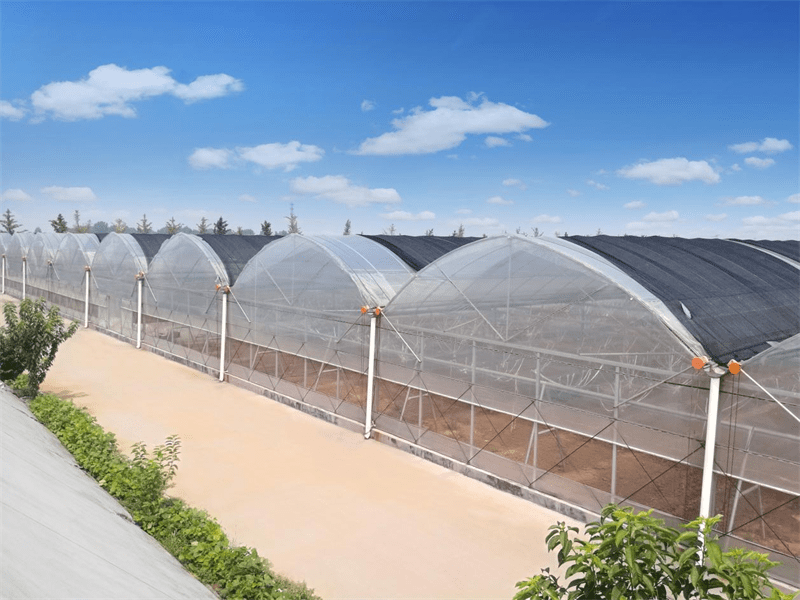
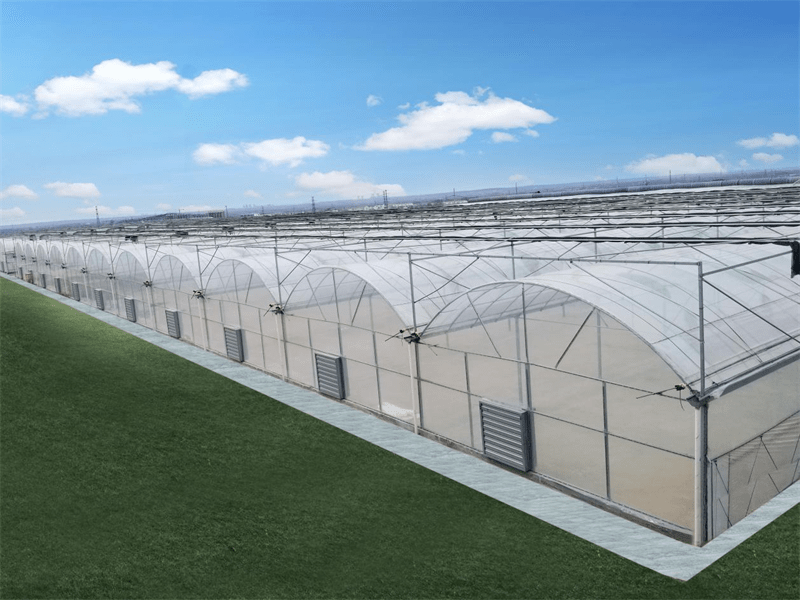
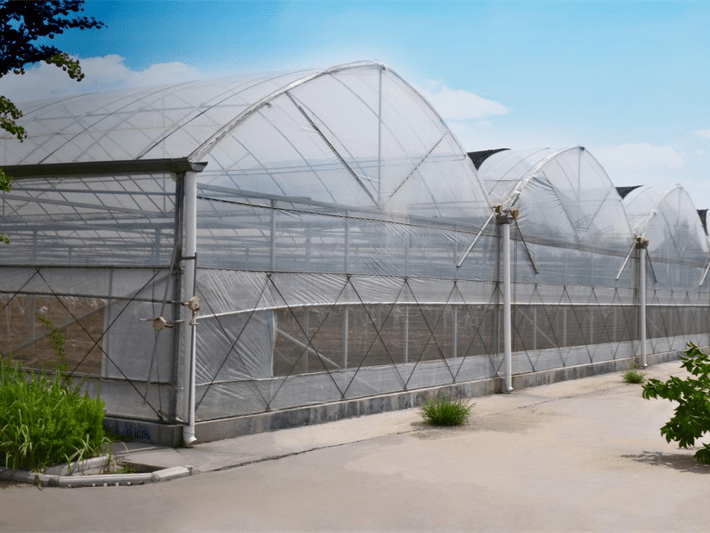
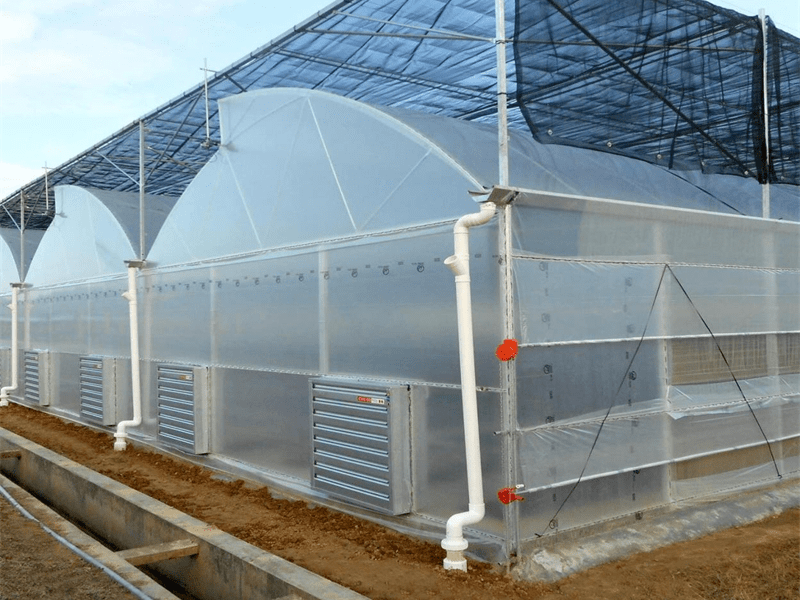
Multi-Span Film Agricultural Greenhouse
description2
Characteristics of multi-span film greenhouses
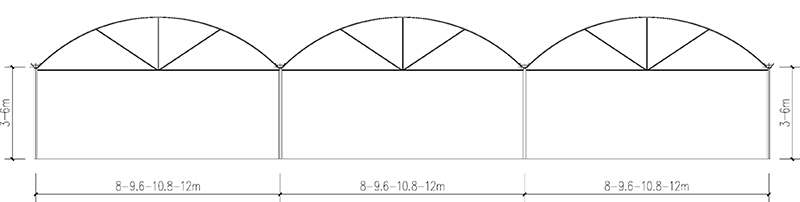
Parameters
| Type | Multi-span Film Greenhouse |
| Span Width | 8m/9.6m/10.8/12m |
| Bay width | 4m |
| Gutter height | 3-6m |
| Snow load | 0.15KN/㎡ |
| Wind load | 0.35KN/㎡ |
| Hanging load | 15KG/M2 |
| Max rainfall discharge | 140 mm/h |
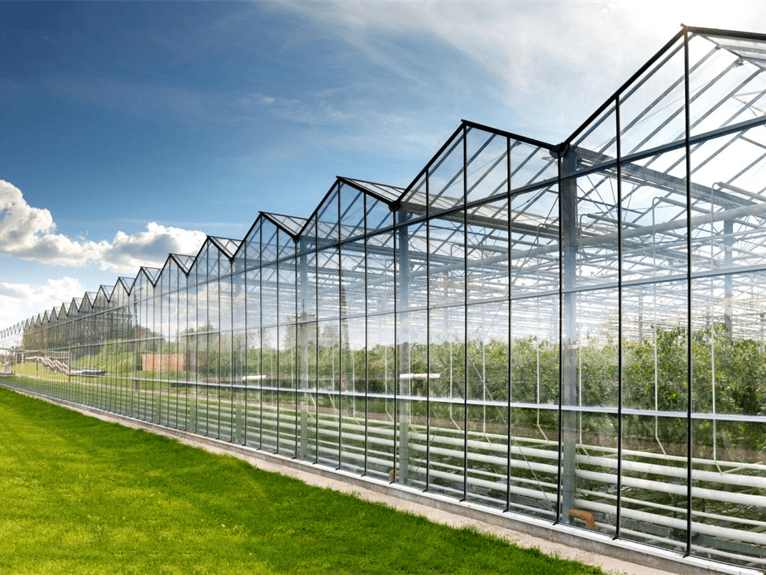
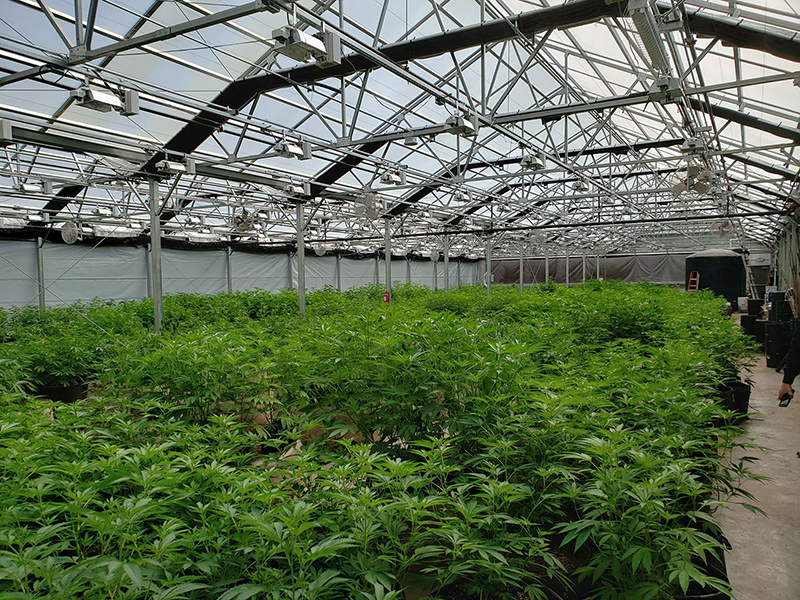
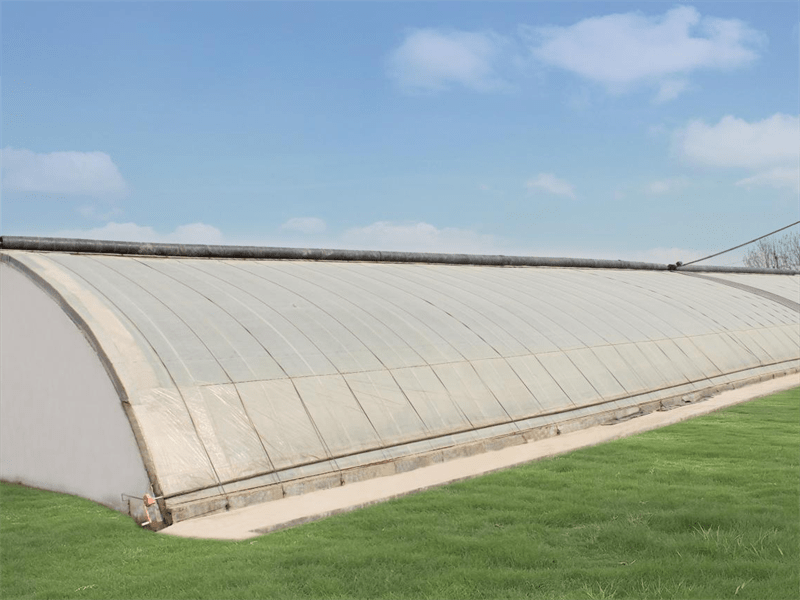
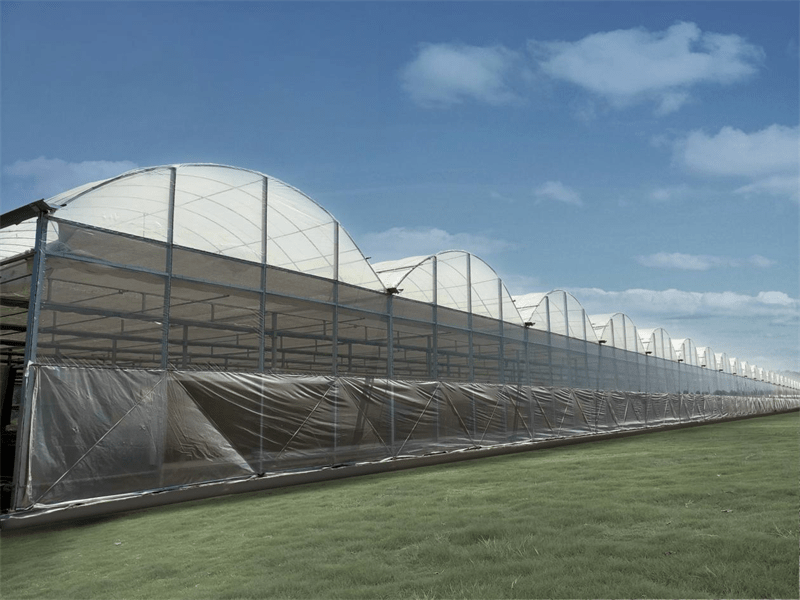
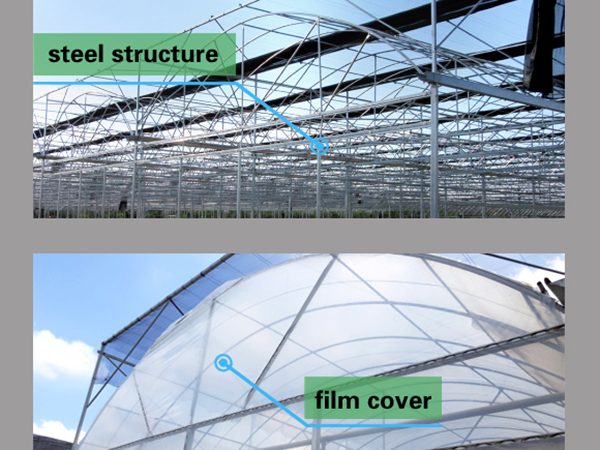
Greenhouse Cover&Structure
- 1. Steel Structure
- The steel structure's material is high-quality carbon steel that adheres to the national standard and undergoes processing in accordance with specific technical requirements. Both the inside and outside of the hot galvanized steel need to meet national standards for quality products. The galvanized layer should have uniform thickness without any burrs and should be at least 60 microns thick.
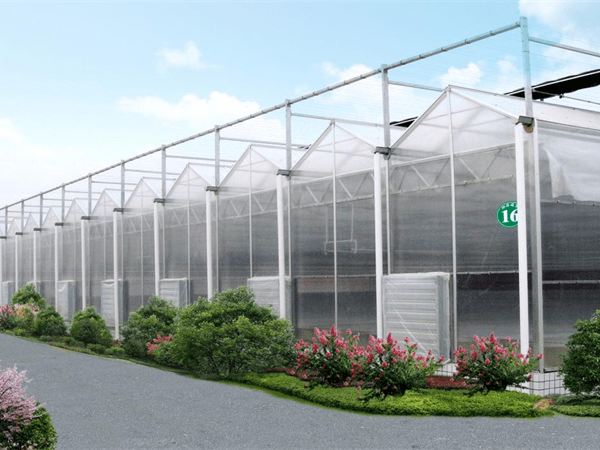
- 2. Cover material
- The film cover is typically made using either PE film or PO film, with the former produced using 3-layer technology and the latter using 5-layer technology. All the films are coated with UV protection and possess anti-drip and anti-aging characteristics. The film is available in thickness options of 120 microns, 150 microns, or 200 microns.
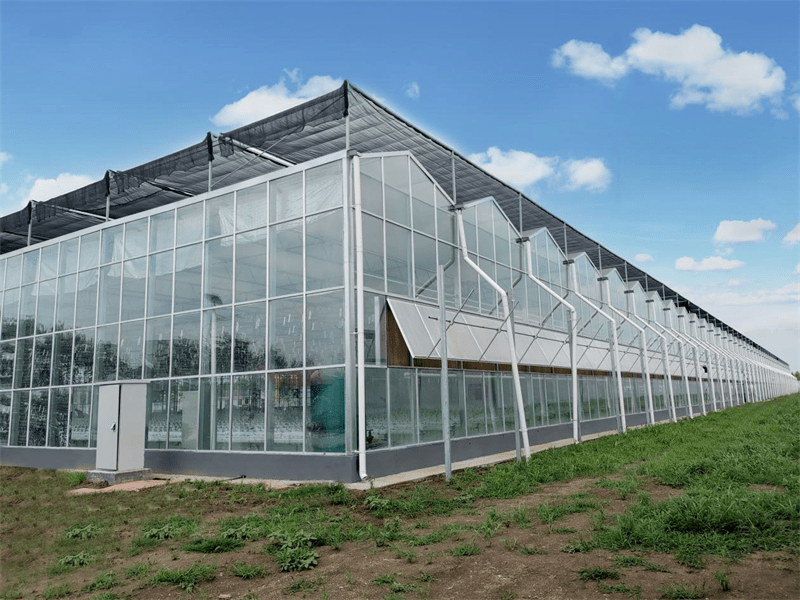
Inner Sunshade&Warming System
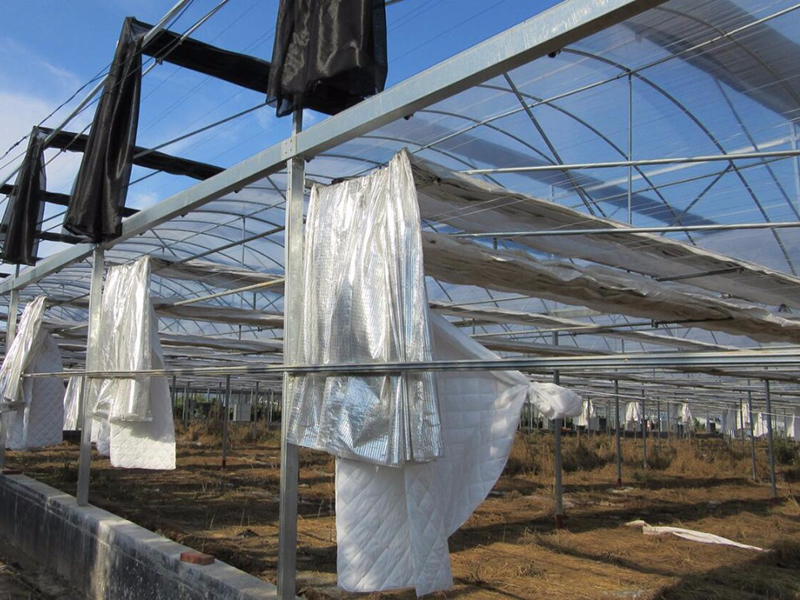

The system involves the installation of an inner sunshade net inside the greenhouse. During the summer, it is capable of lowering the internal temperature, while in winter and at night, it can prevent heat loss. The system offers two variations: ventilation-type and thermal insulation-type, providing options for managing the greenhouse environment.
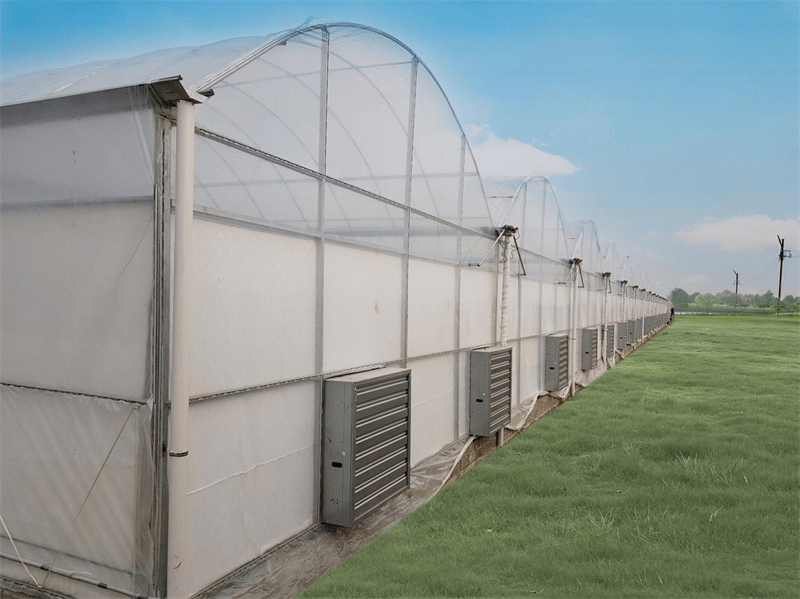
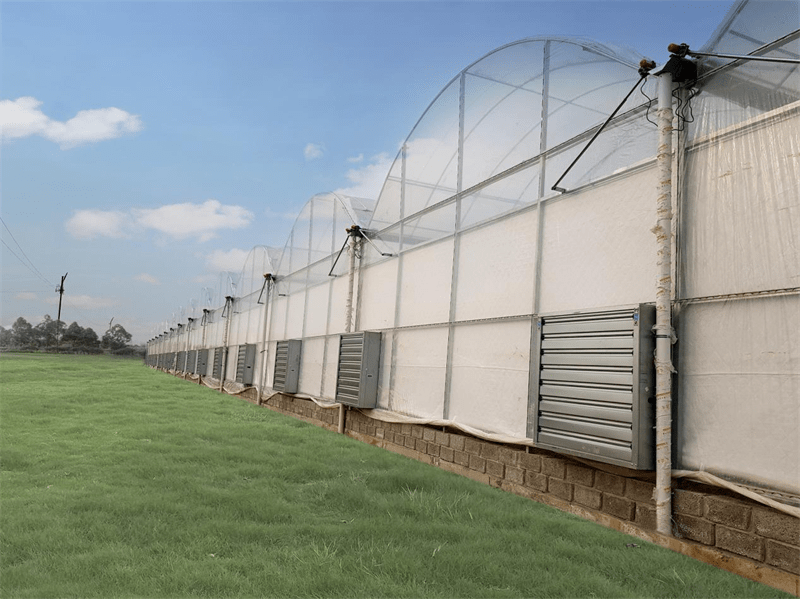
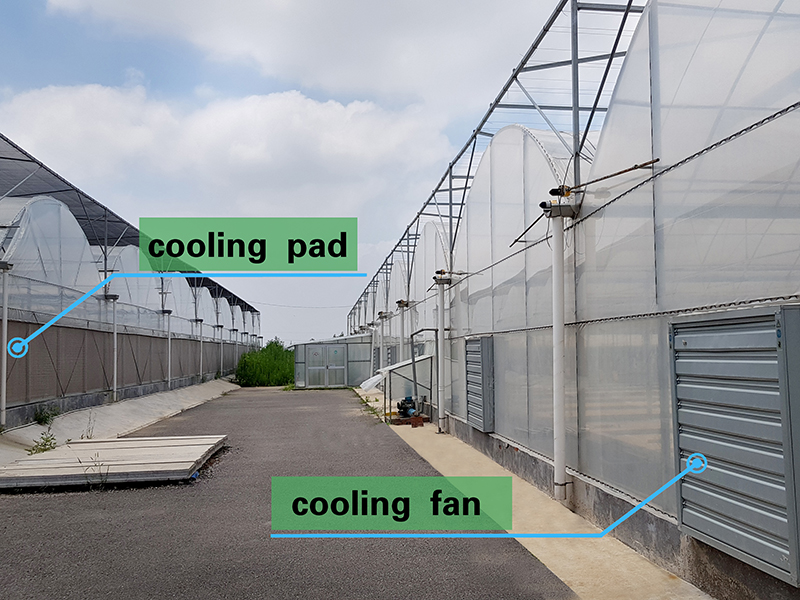
Cooling System
The cooling system uses water evaporation to decrease temperature. It includes high-quality cooling pads and powerful fans. The key component of the cooling system is the evaporative cooling pads, which are made of corrugated fiber paper and are corrosion-resistant with a long working life due to a special chemical composition in the raw material. These special cooling pads ensure full saturation with water. As air passes through the pads, the exchange of water and air on the surface changes hot air into cool air, while also humidifying and cooling the air.

Ventilation System
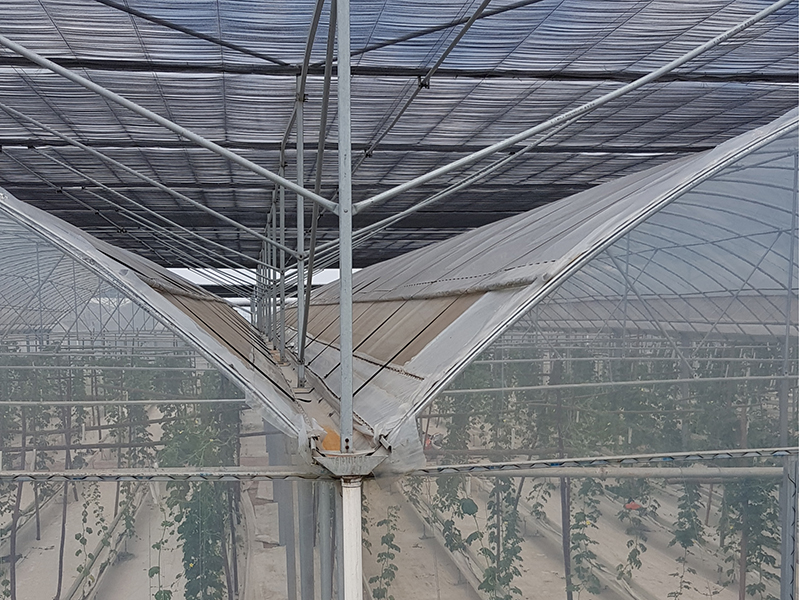

Greenhouse ventilation systems are categorized into two types: natural ventilation and forced ventilation. In film greenhouses, natural ventilation is achieved using roll membrane ventilation on both the roof and sides. Meanwhile, sawtooth greenhouses primarily utilize roll film ventilation for roof ventilation. Insect-proof nets with a 60 mesh size are fitted at the ventilation openings to prevent the entry of insects. Furthermore, ventilation systems can be tailored to meet specific customer preferences and the requirements of different growing conditions.
Light Compensating System
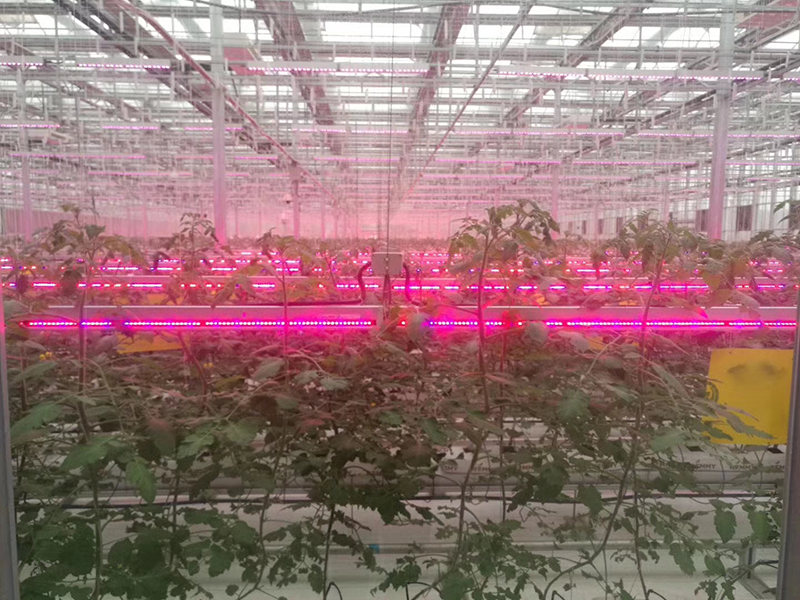

Greenhouse compensating light, also known as plant light, provides the necessary artificial light for plants to grow and develop, independent of natural sunlight. This approach aligns with the natural laws governing plant growth and the concept of plants using sunlight for photosynthesis. Currently, the majority of farmers use high pressure sodium lamps and LED lamps to provide this essential light source for their plants.
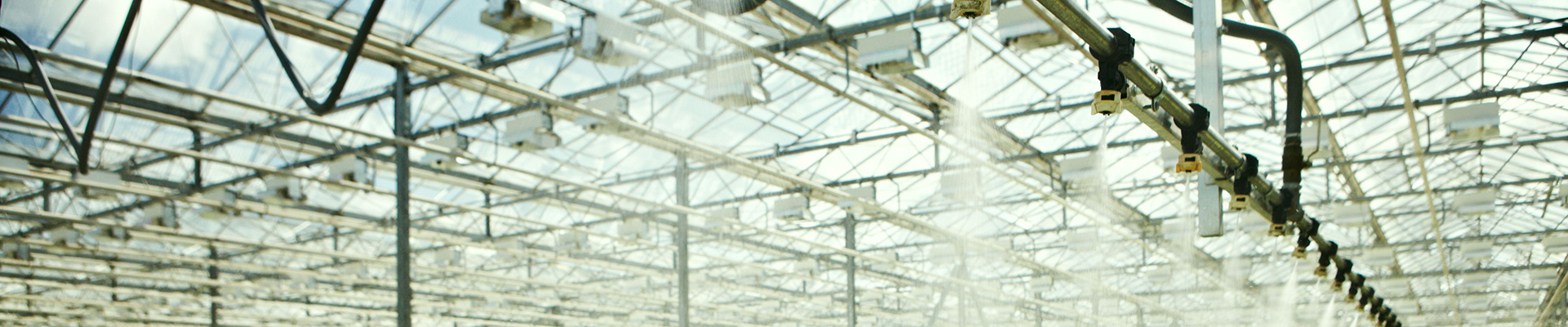
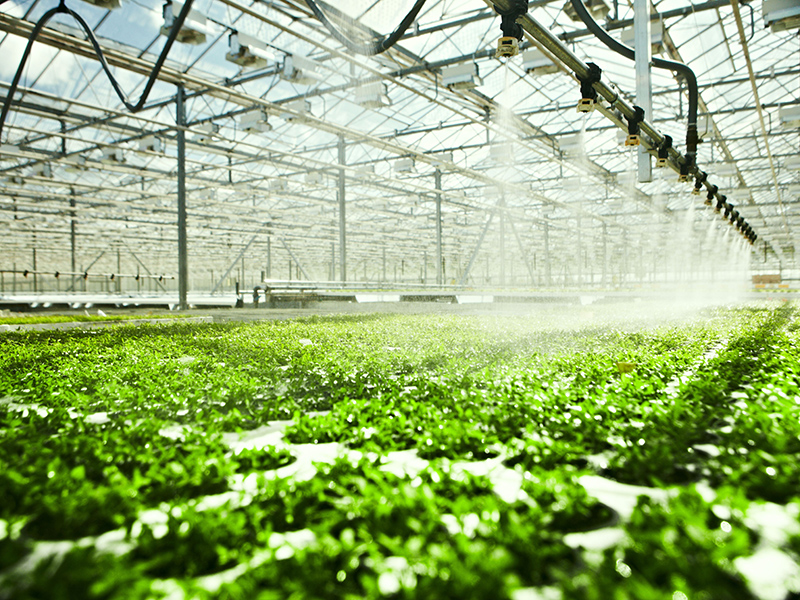
Irrigation System
We provide two types of irrigation systems: drip irrigation and spray irrigation. This allows for the selection of the most suitable system for your greenhouse based on your specific requirements.

Nursery Bed System
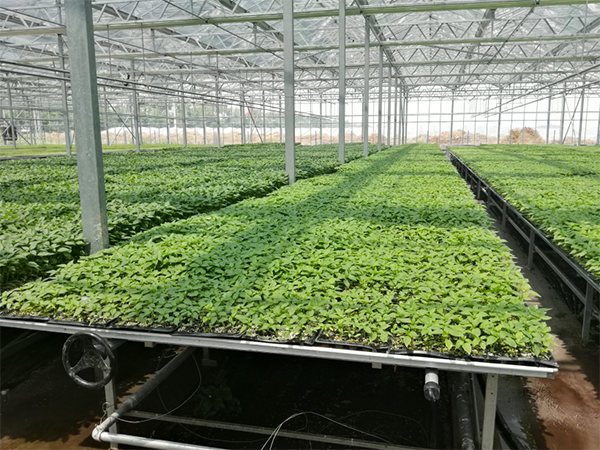

The nursery bed is comprised of both a fixed bed and a movable bed. The specifications for the movable nursery bed include a standard seedbed height of 0.75m, with the ability to be slightly adjusted. Its standard width is 1.65m, with the option to be altered to match the width of the greenhouse, and the length can be customized based on user requirements. The movable bed grid measures 130mm x 30mm (length x width) and is made of hot-dip galvanized material, offering high corrosion resistance, strong load-bearing capacity, and a long service life. In contrast, the fixed bed is 16m in length, 1.4m wide, and has a height of 0.75m.
CO2 Control System
The primary objective is to monitor the CO2 concentration within the greenhouse in real-time to ensure that it consistently falls within the range conducive to crop growth. This process involves the use of a CO2 detector and CO2 generator as the main components. The CO2 sensor serves as a detection device for measuring CO2 concentration, allowing for ongoing monitoring of the greenhouse's environmental parameters. Adjustments are then made based on the monitoring results to maintain an optimal growth environment for plants.